What’s up, everyone!
This week I’ll have a look at tamper protection, a feature of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. The idea here is to make sure that certain security settings are always on so that your endpoint is safe. Let’s take real-time protection for example. The endpoint is protected against virusses and malware in real-time when users are working on the endpoint as long as real-time protection is enabled. But the endpoint becomes susceptible to threats if real-time protection is disabled. That’s where tamper protection comes in. You can prevent changes to certain security settings, like real-time protection, once this feature is enabled.
Tamper protection is part of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint so you can use it on different endpoints and manage it via different solutions. In this post I will demo tamper protection using Microsoft Intune and Windows 365 Cloud PCs. Therefore I welcome you to tamper protection; the Microsoft Intune and Windows 365 edition!
Prerequisites
The following are prerequisites if you want to configure and use tamper protection:
- Devices have to be enrolled into Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
- Devices have to use anti-malware platform v4.4.2010.7 or higher and anti-malware engine v1.1.17600.5 or higher
- Devices have to run;
- Windows 10/11 (Multi-session is supported)
- Windows Server 2022, Server 2019, Windows Server v1803 or later
- Windows Server 2012/2016 R2
- macOS v11 or higher
- A license for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint;
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 1
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus
- Microsoft Defender for Business
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium
- Windows 365
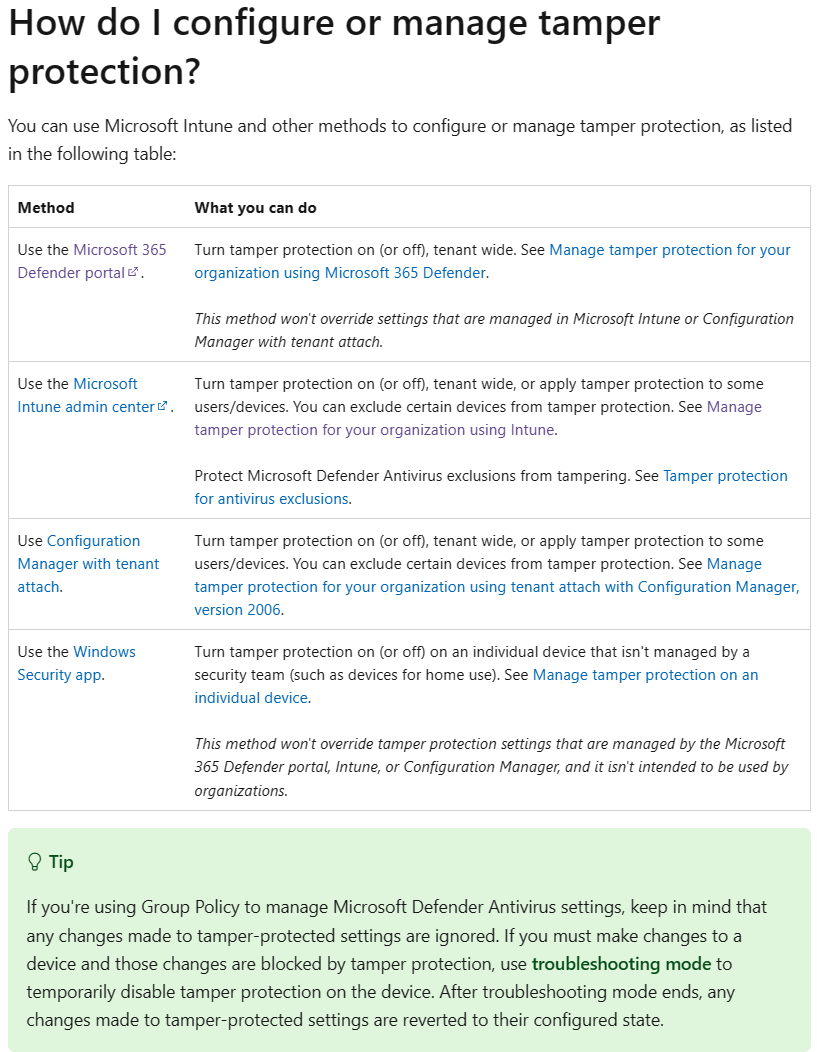
How to manage tamper protection?
There are a couple of ways you can manage tamper protection. Since Microsoft already documented these options pretty well, I won’t bore you with a recap. Instead I will add a screenshot and link you to the correct documentation:
In this post I will have a look at managing tamper protection with Microsoft Intune.
What 'certain' security settings are protected?
Let’s have a look at each component that is protected by tampering protection and add a short description:
Virus and threat protection remains turned enabled
Virus and threat protection scans your endpoint for known threats and you can use it to run a quick or full scan.
Real-time protection remains turned on
Real-time protection means that Defender will scan your endpoint for threats during regular use.
Behavior monitoring remains turned on
Behavior monitoring looks how a process behaves once it’s being executed. It can stop a threat even when it’s already running.
Antivirus protection, including IOfficeAntivirus, stays enabled
This is part of keeping Defender up and running.
Cloud Protection stays enabled
Cloud Protection enhances the standard real-time protection by adding rapid identification of new threats.
Security intelligence updates occurs
Security intelligence is used by Microsoft in their anti malware products. You can get updates through Windows Updates.
Automatic actions are taken on detected threats
Defender can remediate a threat once it’s found.
Notifications are visible in the Windows Security app on Windows devices
This one is pretty self-explanatory.
Archived files are scanned
This will make sure that archives such as .zip files are scanned for threats.
Now that we know what tamper protection is, we can move on to …
How to configure tamper protection using Microsoft Intune
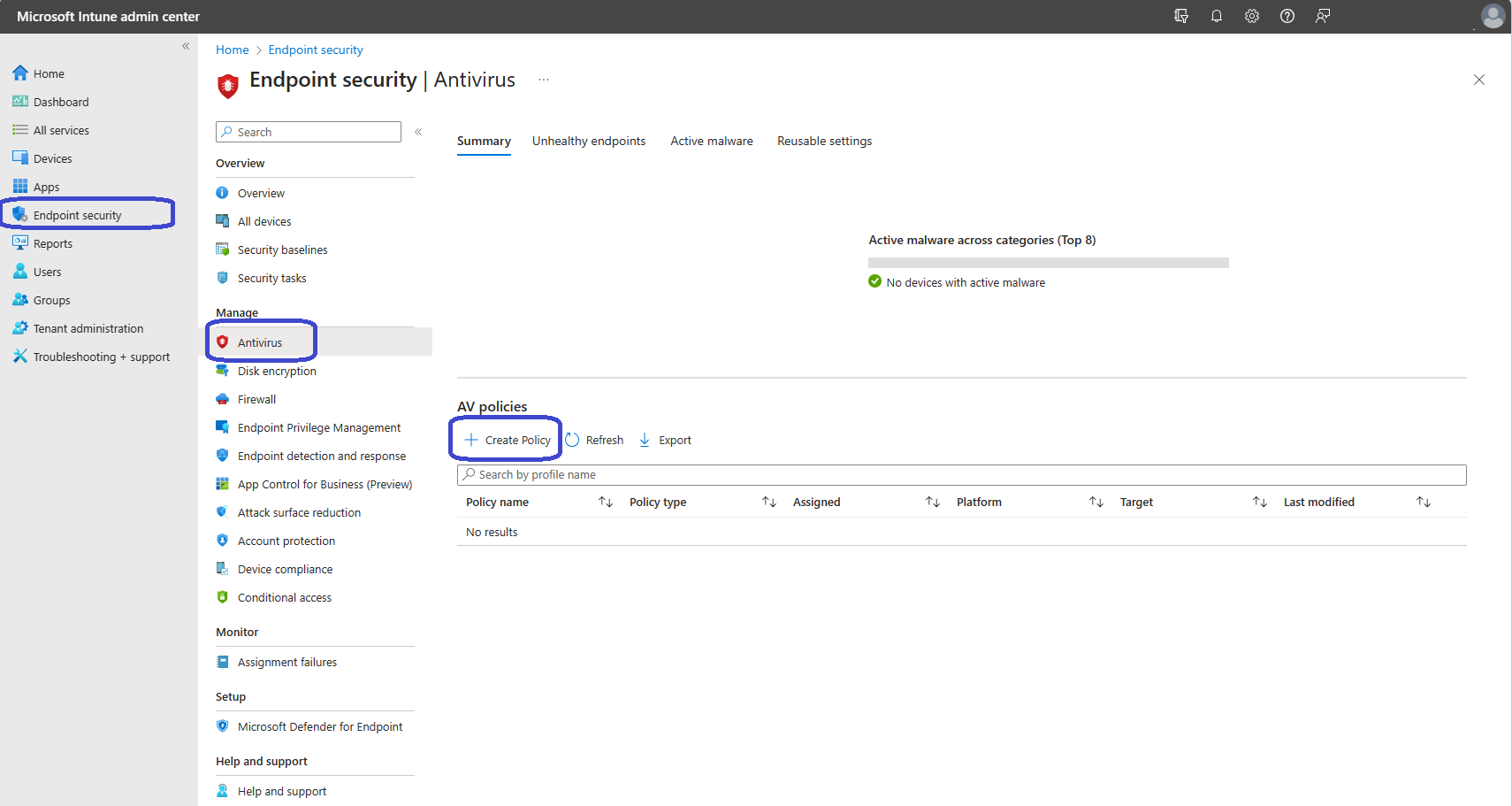
Now that your endpoint is enrolled into Microsoft Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, there’s only one thing left to do and that is to create a policy.
From the Microsoft Intune admin center, Endpoint security, Antivirus, under the AV policies click the + Create policy button.
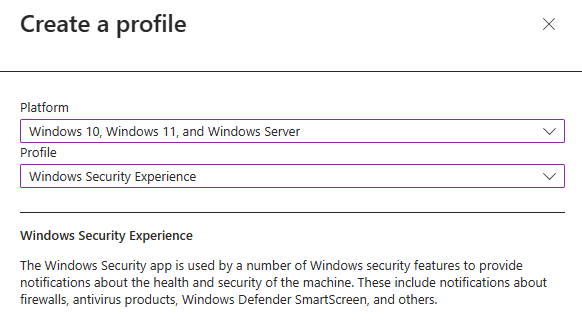
Next you will need to select Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server as the platform and Window Security Experiences as the Profile.
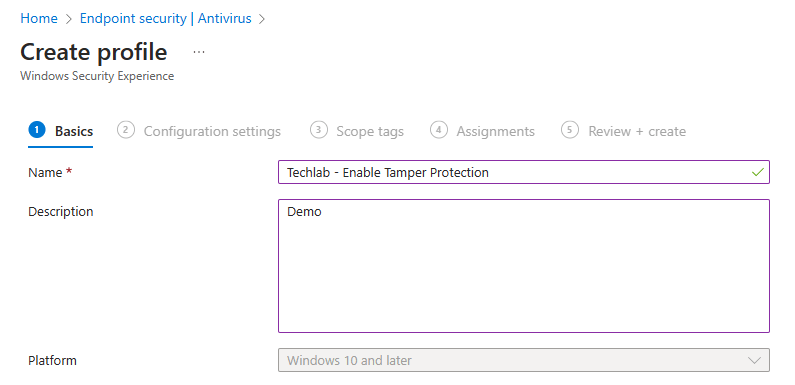
In the next step we can give the policy a name and a description.
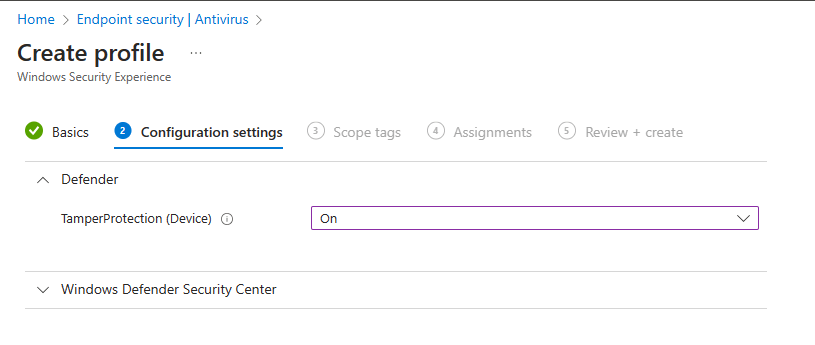
In the Configuration settings step we only have to look at the Defender part. It has a setting called TamperProtection (Device) and we need to set it to On.
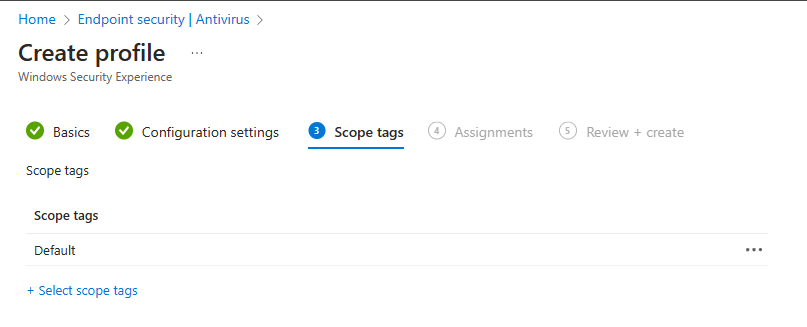
In step 3 you can assign scope tags if you want.
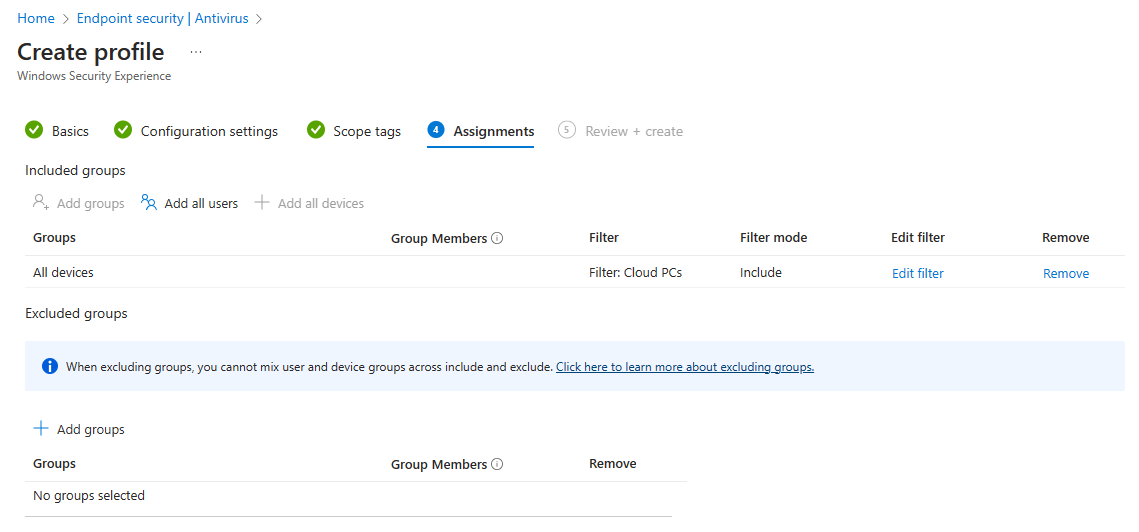
In step 4 you can assign the policy to all devices or a group with the devices. And yes, nowadays tamper protection is also supported for Cloud PCs!
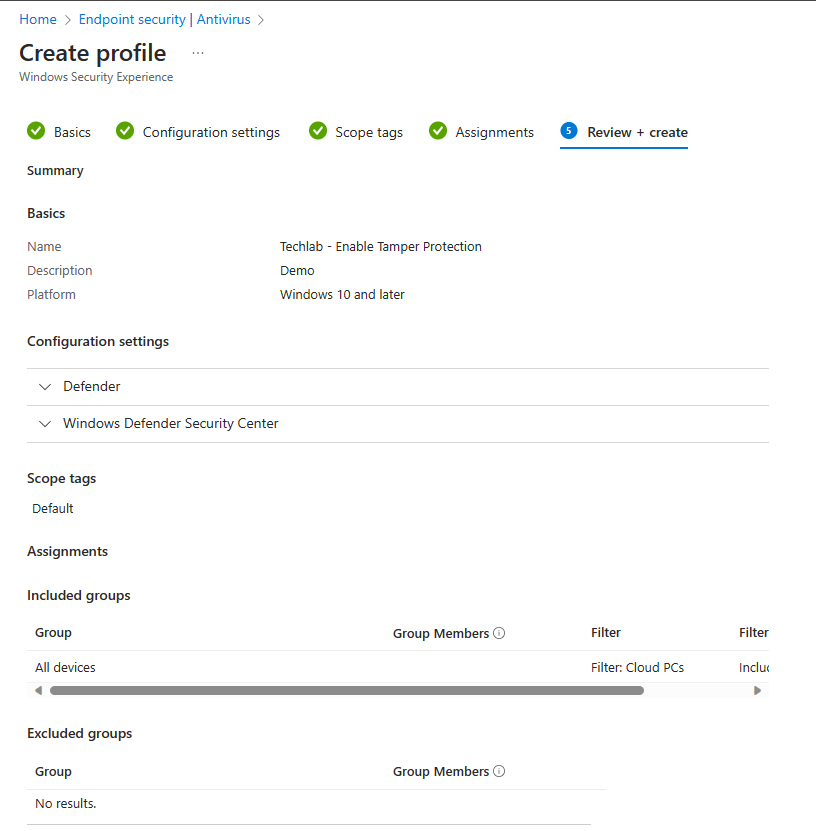
And as always you get a nice moment to review your awesome work and create the policy if you are happy with it.
And there you go; tamper protection is up and running. Of course this is just a basic demo on how to set it up. My advice would be to read up on all the documentation on Microsoft Learn if you are interested to enable tamper protection in a real world scenario because there are some things that you should be aware of. Things like using antivirus exclusions or how to determine if tamper protection is running on an endpoint.
Resources
I used the following resources for this post:
Manage tamper protection for your organization using Microsoft Intune | Microsoft Learn
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on tamper protection | Microsoft Learn
What’s new in Windows 365 Enterprise | Microsoft Learn (7th of August 2023)